The reciprocating air compressor, also known as the piston air compressor, is a widely used piece of equipment in various industries. Its working principle is based on a simple yet efficient design—utilizing the back-and-forth motion of a piston within a cylinder to compress air. This technology dates back to the early 19th century and gained widespread adoption during the Industrial Revolution. Over the years, the piston air compressor has undergone multiple technological iterations, yet it remains popular due to its simple structure, mature technology, and high reliability.
Despite having been around for centuries, modern reciprocating compressors have seen significant improvements in energy efficiency, stability, and environmental friendliness. Whether in manufacturing, automotive, or energy production, reciprocating compressors continue to play an essential role in various industries, proving their irreplaceable value in daily operations.
What is a Reciprocating Air Compressor?

A reciprocating air compressor is a type of positive displacement compressor that uses a piston and cylinder system to compress air. The air is then either stored or distributed for use in different processes. This mechanical design relies on the reciprocating motion of the piston within the cylinder to compress air effectively. This makes it a popular choice for applications requiring high-pressure output, such as in manufacturing and industrial operations.
How Does a Reciprocating Air Compressor Work?
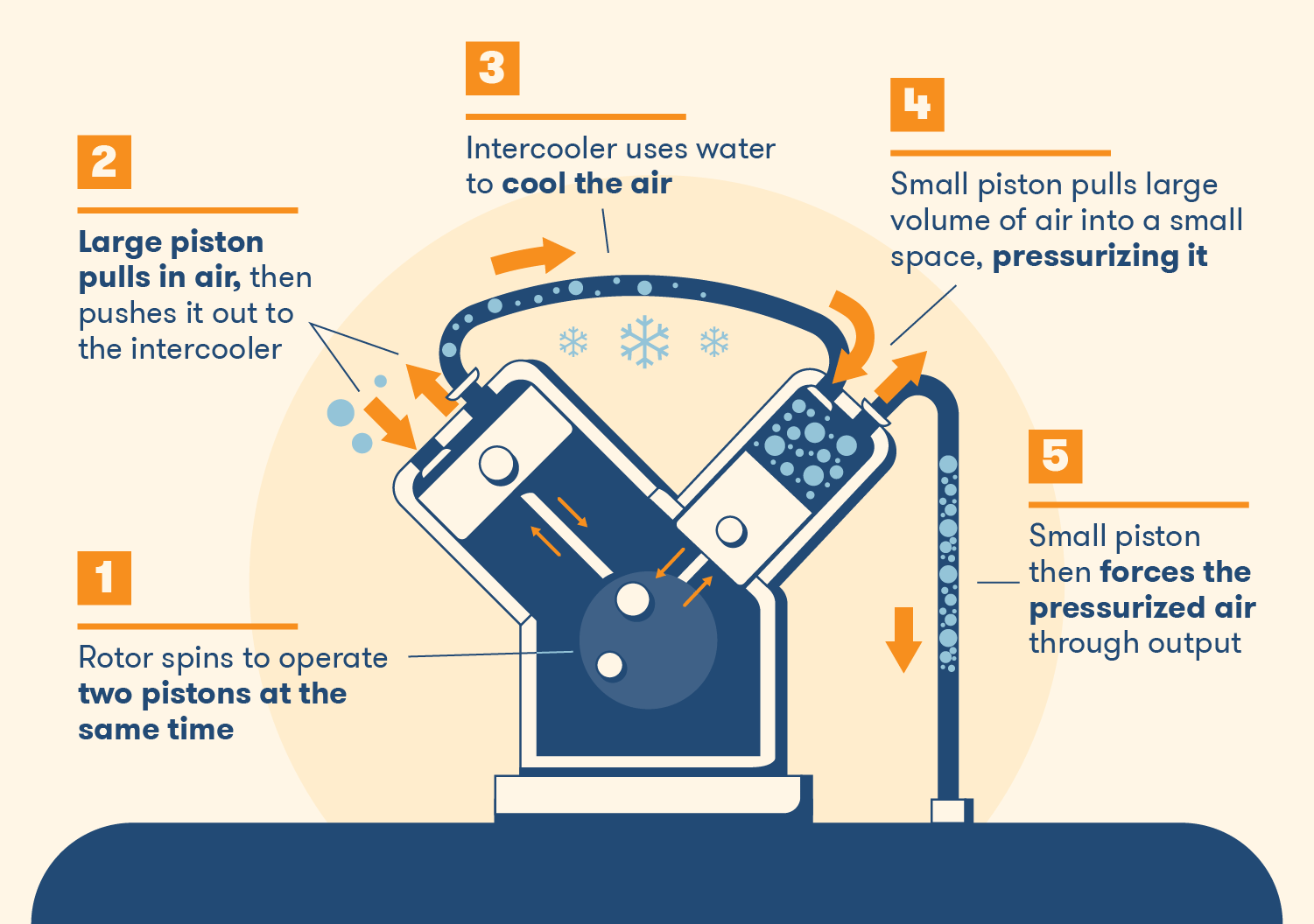
The process begins when the intake valve opens, allowing ambient air to enter the cylinder. As the piston moves upward, the air is compressed, and once the piston reaches the top, the exhaust valve opens to release the pressurized air into the system. This cycle of intake, compression, and exhaust repeats constantly, ensuring a continuous supply of compressed air for various applications.
The efficiency of the compressor largely depends on factors such as the speed of the piston and the valve design. Modern reciprocating compressors often feature advanced components like pressure regulators and cooling systems that optimize the cycle performance.
Advantages of Reciprocating Air Compressors
Reciprocating air compressors offer numerous benefits, making them a versatile and valuable tool for industries that require compressed air:
- High Pressure Output: These compressors can produce extremely high air pressures (up to 500 psi or more), ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Durability: Thanks to their simple and robust mechanical design, reciprocating compressors tend to last longer and require less maintenance compared to other compressor types.
- Energy Efficiency: When used optimally, reciprocating compressors are highly energy-efficient, helping businesses lower operational costs.
- Compact and Cost-Effective: These compressors are usually more affordable in terms of initial investment compared to other types, making them an excellent choice for smaller operations.
Common Applications of Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors are versatile machines with a wide range of applications across various industries. Due to their ability to handle high pressures and their relatively simple mechanical design, these compressors are often the go-to choice for applications that require robust, reliable air compression. Here are some of the most common industries and applications that rely on reciprocating compressors:
Manufacturing Industry
Reciprocating compressors are used extensively in manufacturing processes that require compressed air for powering machinery, tools, and other equipment. From automotive factories to food and beverage production, these compressors help power everything from pneumatic tools to conveyor systems, ensuring smooth production lines and increased productivity.Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, reciprocating compressors are frequently used in various systems, such as vehicle air conditioning, paint shops, and assembly lines. They provide the high-pressure air needed for spraying paint, powering pneumatic tools, and even controlling automated machinery within production facilities.Oil and Gas Industry
In oil and gas exploration and production, reciprocating compressors play a vital role in gas compression. They are used to boost the pressure of natural gas for transportation through pipelines or for the operation of other equipment in refineries and processing plants. The ability to work with high-pressure gases makes these compressors indispensable in this industry.Energy and Power Generation
Reciprocating compressors are also used in power plants, particularly in gas turbine and steam turbine systems, where they help increase the pressure of air and gases for combustion. The energy sector relies on these compressors for various processes that involve the compression of air, gases, and even liquids under high pressure.
Technological Advancements and Sustainability in Reciprocating Compressors
Recent innovations in reciprocating compressor technology have made these machines more efficient and environmentally friendly. For example, Variable Speed Drive (VSD) technology helps control the compressor’s speed, reducing energy consumption during periods of low demand. Additionally, many new models feature eco-friendly components and refrigerants that comply with global sustainability standards.
- Proper Maintenance for Reciprocating Air Compressors
To maintain peak performance and prolong the life of reciprocating compressors, regular maintenance is crucial:
- Lubrication: Ensure the compressor has proper oil levels and lubrication to minimize wear and tear on the internal components.
- Cleaning: Keep the cooling system and intake filters clean to avoid overheating and clogging, which can affect efficiency.
- Inspection of Valves: Regularly inspect the intake and exhaust valves to ensure they function correctly and prevent air leaks.
- Monitoring Pressure Levels: Consistently monitor the pressure levels to avoid system overloading and ensure that the compressor is working within optimal parameters.
How to Choose the Right Reciprocating Air Compressor
Choosing the right reciprocating air compressor for your specific application can significantly improve the efficiency, longevity, and performance of your operations. There are several key factors to consider when selecting the ideal compressor. These include pressure requirements, flow capacity, power source, and the specific needs of your industry. Here’s a more detailed look at the important factors to consider:
Pressure Requirements
The pressure level required for your application is one of the most crucial factors in selecting the right compressor. For instance, industries such as blow molding, which require high-pressure air to shape plastic materials, typically demand compressors capable of delivering pressure levels of around 150 to 200 psi. This ensures that the air is sufficiently pressurized to mold the plastic into the desired shape effectively.Example: In plastic blow molding, a compressor with a 200 psi capacity would be suitable for shaping plastic bottles or containers, as the process requires higher pressures to inflate the material evenly.
Flow Capacity (CFM)
Flow capacity, often measured in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM), refers to the amount of air the compressor can deliver. Different applications require different flow rates. For example, large-scale manufacturing operations that use pneumatic tools extensively may require a compressor with a high CFM rating.Example: In a factory producing automotive parts, a compressor with a flow rate of 100 CFM may be required to power multiple tools simultaneously without compromising performance.
Power Source
Reciprocating compressors can run on a variety of power sources, including electricity, gasoline, or diesel fuel. The choice depends on factors such as the availability of power, portability, and energy costs. For example, electric-powered compressors are commonly used in stationary settings where a reliable electricity supply is available, while gasoline or diesel-powered compressors are preferred in remote or mobile applications.Example: A diesel-powered reciprocating compressor is ideal for use on construction sites where access to electricity may be limited.
Cost and Maintenance
While purchasing a reciprocating compressor, it’s important to consider both the initial cost and the long-term maintenance costs. Compressors with simple designs and fewer components tend to have lower maintenance costs. However, it’s crucial to assess the cost-benefit relationship based on the expected operational life and performance of the machine.Example: For small-scale applications like small automotive workshops, a cost-effective, lower-maintenance compressor could suffice, while large-scale operations might require a more robust and expensive model with advanced features.
Ready to take the next step?
Our experts are here to help you find the perfect reciprocating air compressor for your business needs. Whether you’re looking for a quote, detailed product information, or a consultation, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Contact us today for a free consultation and let’s get started on improving your operations with the best compressor solutions.
Or, if you’re ready to dive deeper, download our brochure to learn more about our product features and specifications
FAQs
The lifespan of a reciprocating compressor can vary based on its use and maintenance. On average, with proper maintenance, these compressors can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years. Regular servicing, including oil changes and air filter replacements, can help extend the compressor’s life and ensure optimal performance.
Proper maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your compressor. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Regular lubrication: Ensure the compressor is properly lubricated to reduce wear and tear.
- Filter cleaning/replacement: Regularly clean and replace air intake filters to ensure optimal airflow.
- Valve inspections: Check intake and exhaust valves periodically for wear and proper functioning.
- Pressure monitoring: Regularly monitor the pressure levels to prevent overloading.
Yes, reciprocating compressors are well-suited for large-scale industrial operations that require high pressure and reliable performance. They are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and energy production. For large-scale operations, compressors with higher flow rates (CFM) and pressure capacities (PSI) are available to meet demanding applications.
Modern reciprocating compressors have become more environmentally friendly thanks to innovations in energy efficiency and eco-friendly refrigerants. Additionally, features such as Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) help optimize energy consumption, reducing environmental impact during periods of low demand. Proper maintenance and use of the right lubricants can also contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of these compressors.